Data has become an essential cornerstone in the world of business in respect to decision-making. Two disciplines have emerged in harnessing the power of data: Business Intelligence and Business Analytics. So, if you’re thinking of taking a Business Analytics course to enhance your skills in these areas, it’s vital to understand the differences to make the right and informed decision.
Let’s understand about both of them:
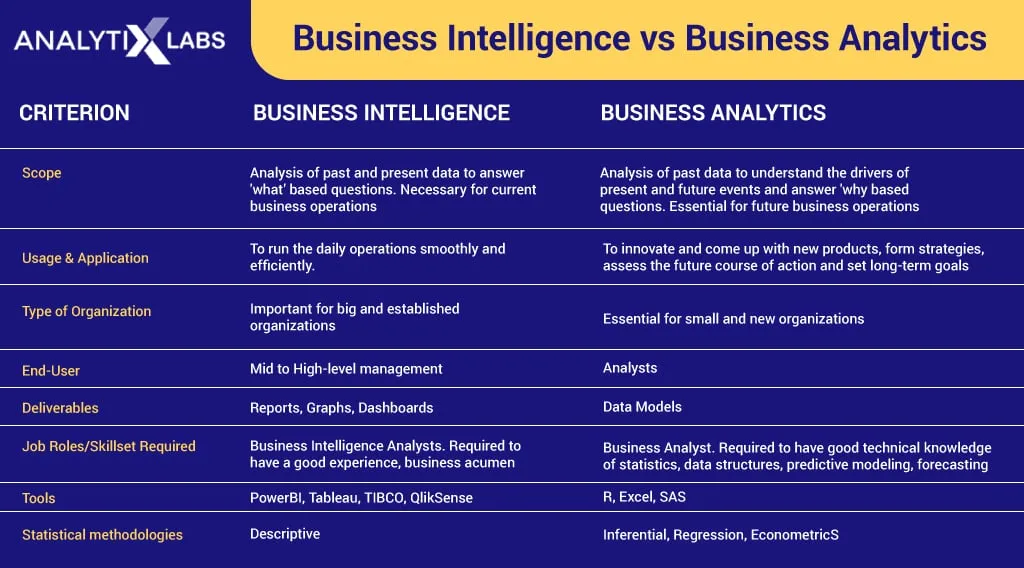
What is Business Intelligence?
Business Intelligence, often abbreviated as BI, primarily focuses on looking backward. It involves collecting, storing, and analyzing historical data to gain deep insights into past performance and business trends. Business Intelligence tools and techniques transform raw data into meaningful information that can then be presented as reports, dashboards, and visualizations.
Characteristics of Business Intelligence:
- Descriptive Analytics
- Data Warehouses
- Static Reporting
- User-Friendly Interfaces
- Decision Support
What is a Business Analytics Course?
Business Intelligence deals with historical data, Business Analytics, or Business Analytics course, focuses on looking forward. BA employs advanced statistical and predictive modeling techniques to forecast future trends, identify opportunities, and make proactive decisions. It aims to answer questions like, “What is likely to happen in the future?” or “What should we do to achieve specific goals?”
Characteristics of Business Analytics Course:
- Dynamic Models
- Machine Learning and Data Science
- Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics
- Real-time Data Analysis
- Data Exploration
Business Intelligence vs Business Analytics: Comparison Table
| Aspect | Business Intelligence (BI) | Business Analytics (BA) |
| Focus | Historical data analysis. | Future-oriented, predictive analysis. |
| Primary Objective | Provide insights into past performance. | Predict future trends and enable proactive decisions. |
| Analytics Type | Descriptive analytics (What happened?). | Predictive and prescriptive analytics (What is likely to happen, and what should we do?). |
| Data Usage | Historical data from data warehouses. | Real-time or near-real-time data, often with dynamic models. |
| Tools | Data visualization tools (e.g., Tableau, Power BI). | Advanced statistical modeling, machine learning, and data science tools. |
| User Base | Business users, managers, and executives. | Data scientists, business analysts, strategic decision-makers. |
| Frequency of Reports | Static, regular reports (daily, weekly, monthly). | Ad hoc and real-time reports as needed. |
| Decision-Making Level | Supports operational decisions. | Supports strategic and tactical decisions. |
| Questions Answered | What happened? | What is likely to happen, and what should we do about it? |
| Skills Emphasized | Data visualization, SQL, data warehousing. | Predictive modeling, data mining, machine learning, data-driven decision-making. |
| Output | Historical reports, dashboards, and charts. | Predictive models, recommendations, and data-driven strategies. |
| Use Cases | Financial reporting, performance analysis. | Market forecasting, customer segmentation, and supply chain optimization. |
| Goal | Understanding past performance. | Gaining a competitive edge through data-driven insights. |
The Bottom Line
Business Intelligence and Business Analytics are essential disciplines in the data-driven business world. BI provides a foundation for understanding past performance and reporting, while Business Analytics or Business Analytics course equips organizations with the tools to predict and shape the future. Choosing a Business Intelligence and Business Analytics course depends on your career aspirations and the skills you want to develop. Whichever path you choose, the ability to work with data effectively is a valuable asset that can open doors to exciting and rewarding career opportunities in today’s data-centric business environment.